# Container Orchestration with Kubernetes **ISAE-SUPAERO, SDD, January 2021** <img src="static/img/sdd-logo.png" width="10%" height=auto> <!--s--> ### [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/what-is-kubernetes/)  Kubernetes manages your containers on a cluster of machine while taking care of - Creation, deletion, and movement of containers - Scheduling (match containers to machines by ressources etc.) - Scaling of containers - Serving of containers through unified endpoints - Monitoring and healing <!--s--> ## Containers Orchestration + containers are a lightweight mechanism for isolating an application's environment + specify the system configuration and libraries to install + avoid conflicts with other applications + each application as a container image which can be executed reliably on any machine + place multiple workloads on the same physical machine or distributed over many machines + orchestration for fail cases of containers or machines + allow for updates without downtime by creating new containers <!--s--> ## Orchestration Design Principles + **Declarative** - describe ideal system state + **Distributed** - use multiple machines for scale + **Microservice** - decouple applications into individual services + **Immutable** - Change image versions, not instances <!--s--> ## Declarative Design + Define the desired state of system in Kubernetes configuration + Allow Kubernetes to compare actual state of system with current state to resolve issues + State in Kubernetes: a collection of objects + Specification for each object from configuration to be checked against status of each object <!--s--> ## Distributed Design + Design applications as a distributed system + Natively allows for scaling by adding more workers + Adapts to cloud or cluster computing, optimize CPU and GPU usage of physical machines + Kubernetes provides unified interface 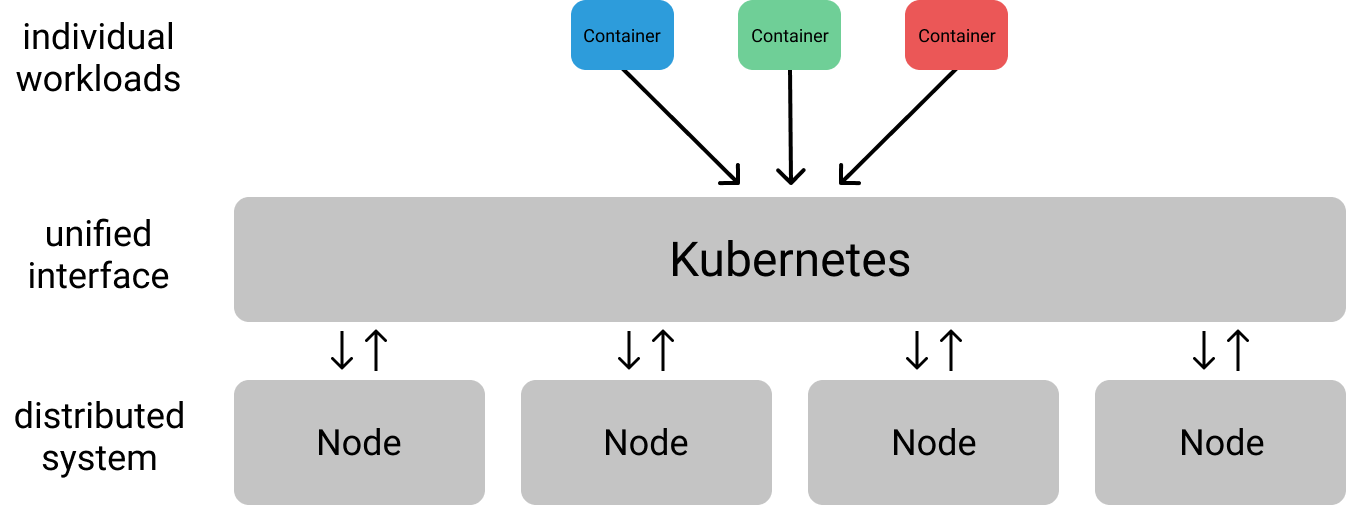 <!--s--> ## Microservice Design 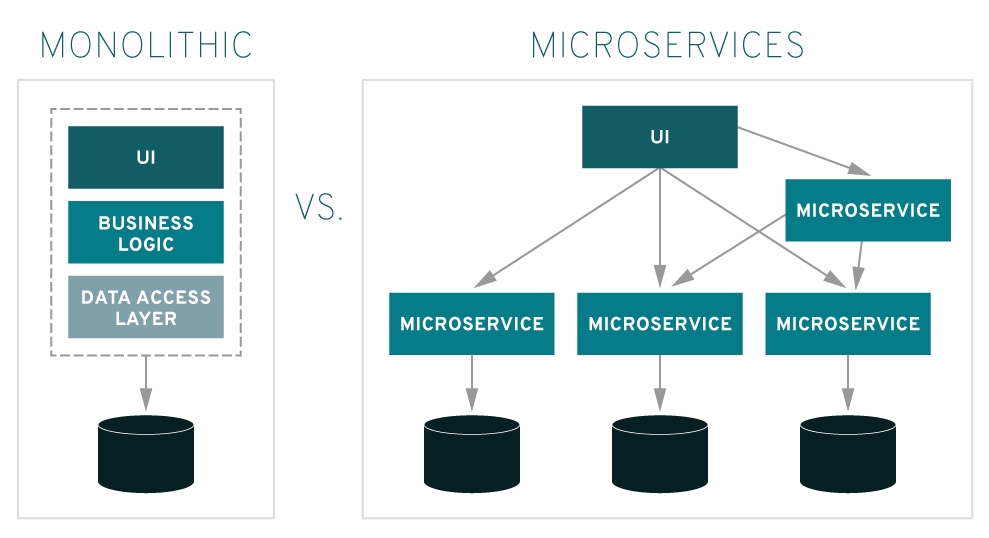 Design applications as independently deployable services: each container should do one thing well <!--s--> ## Immutable Design + For updates, don't make changes directly to a live container + Change the container configuration, deploy new container, terminate previous container + Containers should be **ephemeral** + Allows for accuracy in system health checks + Facilitates rollback to previous states, revision history of images and configuration <!--s--> ## Example Kubernetes System 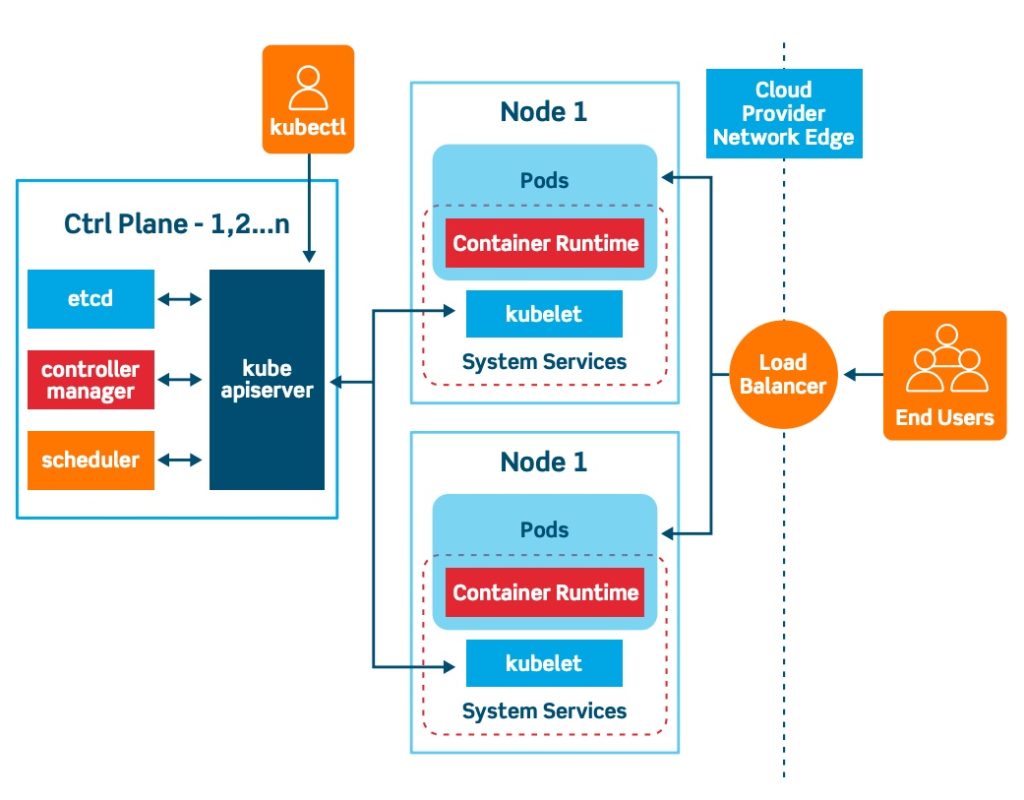 <!-- .element: height="40%" width="40%" --> Different object types: Pod, ReplicaSet, Deployment, Service, Job <!--s--> ## Pod + One or more related containers + Shared networking layer and filesystem volumes + Meant to be ephemeral 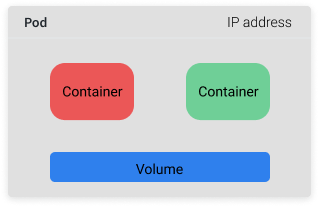<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Deployment + Collection of pods and replicas of pods + Behind the scenes, creates a ReplicaSet 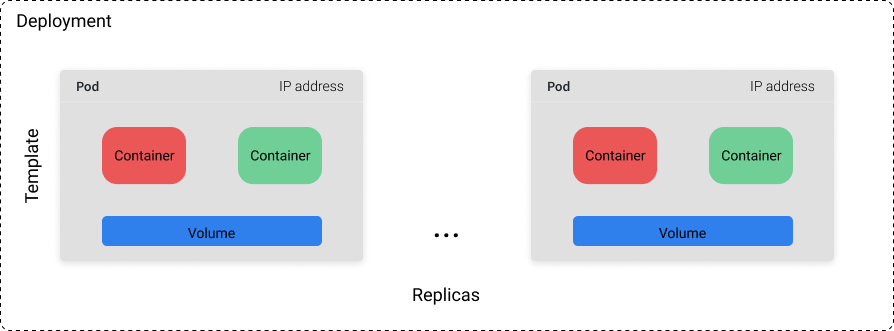<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Pod, Deployment configuration 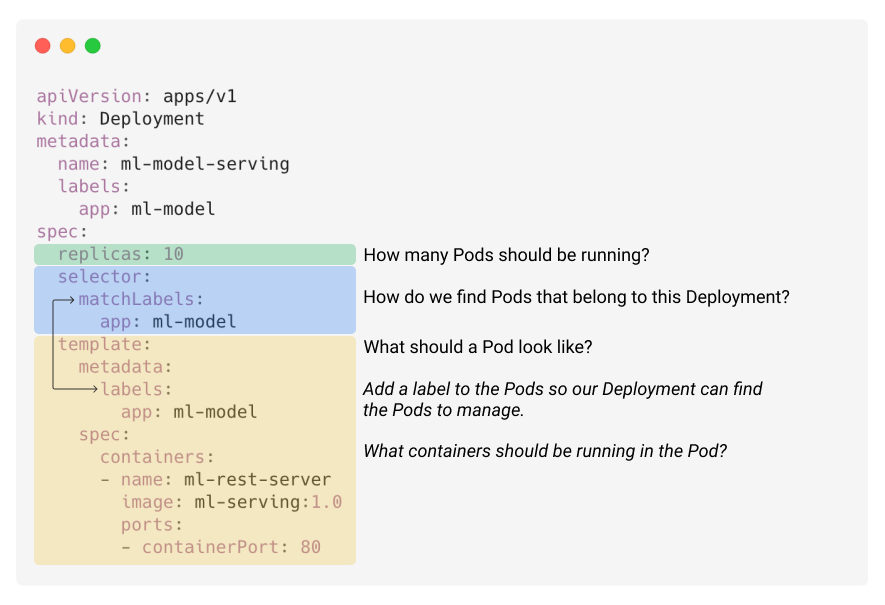<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Updating Deployments 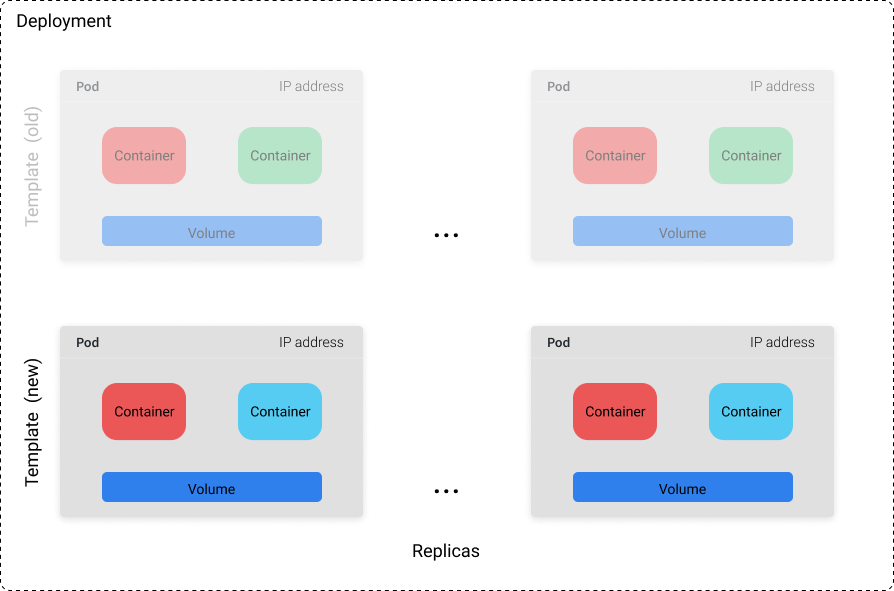<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Service + Ephemeral pods have unique IP addresses, how to maintain traffic during updates? + Services are stable endpoints for communicating with pods + Use key-value pairs to identify pods from Pod metadata 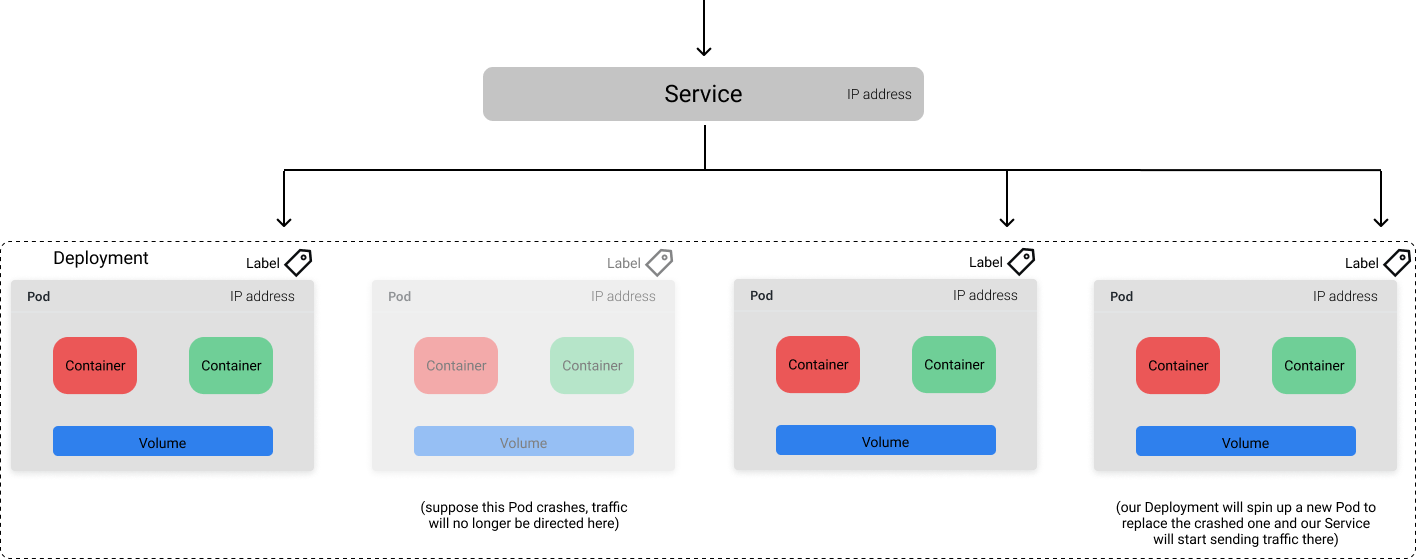<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Service Configuration <!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Ingress + Service: internal endpoints + Ingress: external endpoint 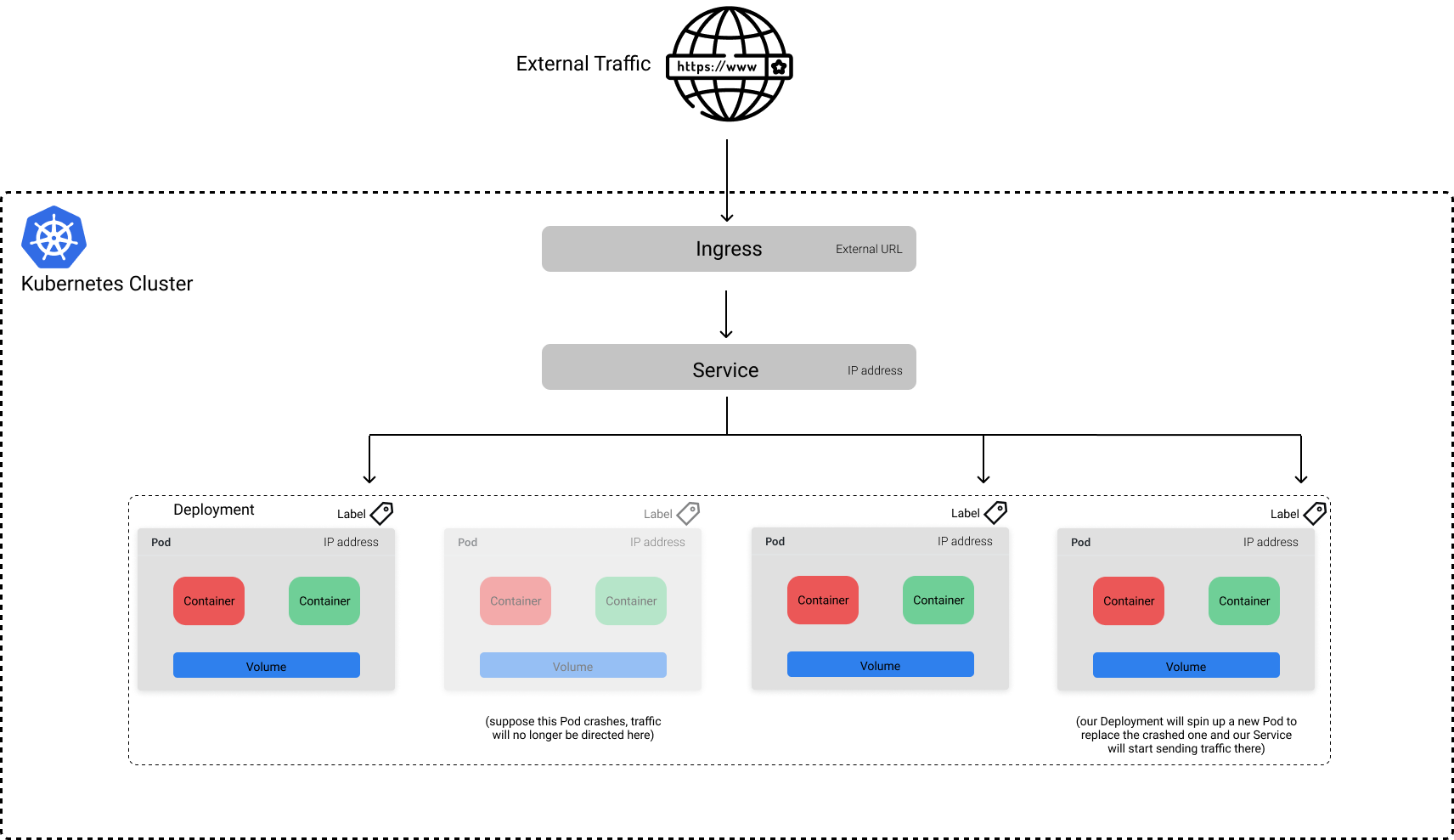<!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> <!--s--> ## Ingress Configuration 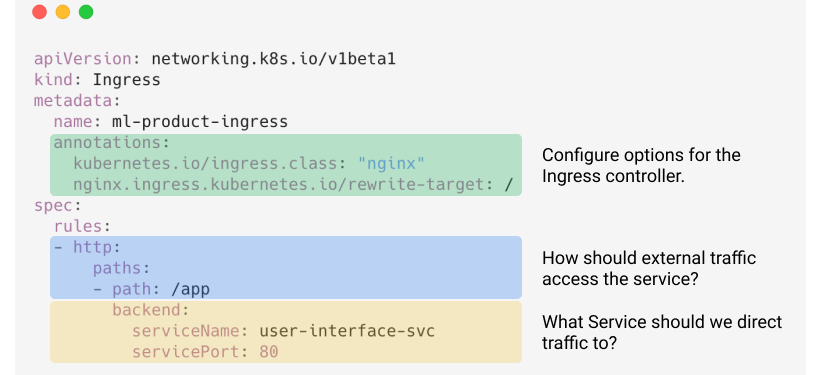 <!--s--> ## Job + Perform a single, discrete task (as opposed to long-running service like a web server) + Daily example: create a container to train a ML model, deploy the model, shut down container + Reliable: if the job crashes, Kubernetes can relaunch until desired state of job completion is acheived 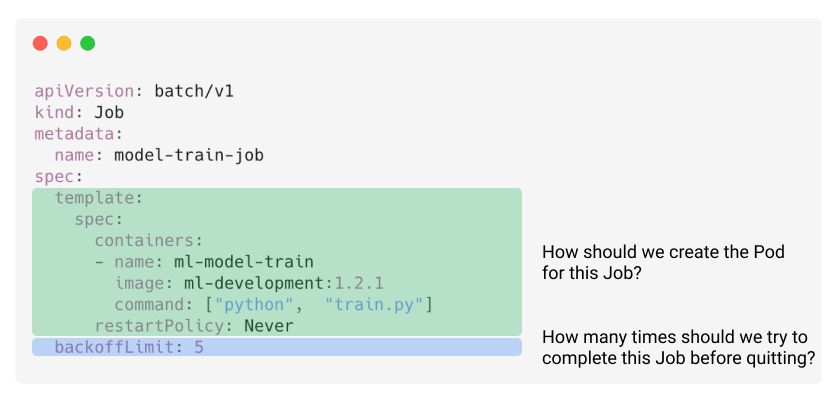 <!--s--> ## Interacting with a cluster + Master node allows for user to control the cluster through API access + On GCP, provided automatically when creating a Kubernetes cluster 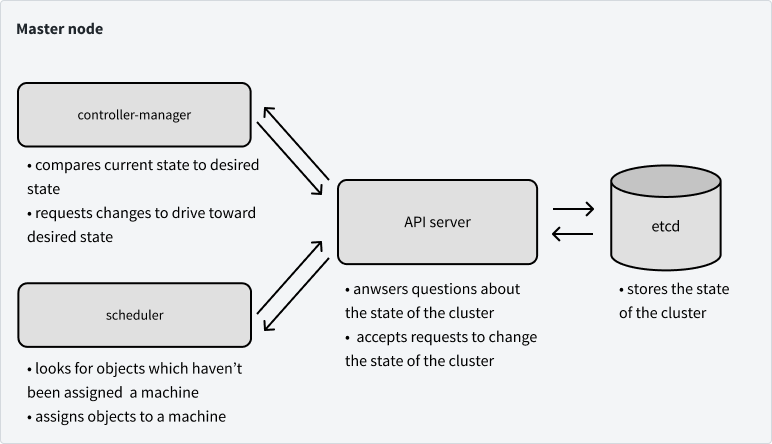 <!--s--> ## Kubernetes System 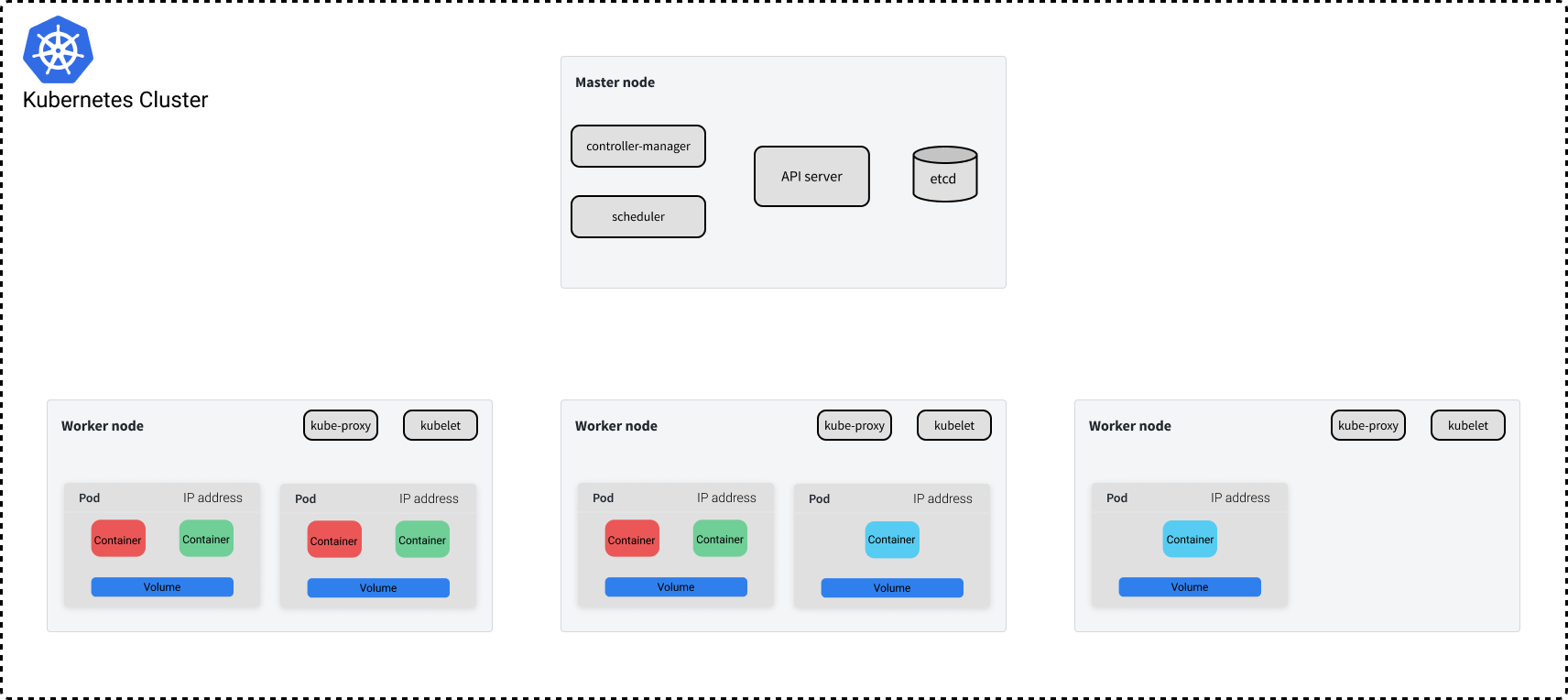 <!--s--> ## Exercise What does the following configuration do? How many workers are used and what do they do? ```yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-deployment labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.14.2 ports: - containerPort: 80 ``` <!--s--> ## Helm  <!-- .element: height="50%" width="50%" --> + similar to `apt` for Ubuntu + allows for live package management on K8S clusters <!--s--> ## Helm Charts (packages) are organized in repositories ``` $ helm repo add stable https://charts.helm.sh/stable ``` ``` $ helm search repo stable NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION stable/acs-engine-autoscaler 2.2.2 2.1.1 DEPRECATED Scales worker nodes within agent pools stable/aerospike 0.2.8 v4.5.0.5 A Helm chart for Aerospike in Kubernetes stable/airflow 4.1.0 1.10.4 Airflow is a platform to programmatically autho... stable/ambassador 4.1.0 0.81.0 A Helm chart for Datawire Ambassador # ... and many more ``` <!--s--> ## Helm Update packages ``` $ helm repo update # Make sure we get the latest list of charts $ helm install stable/mysql --generate-name Released smiling-penguin ``` Provides package information on current cluster ``` $ helm ls NAME VERSION UPDATED STATUS CHART smiling-penguin 1 Wed Sep 28 12:59:46 2016 DEPLOYED mysql-0.1.0 ``` Remove packages from a cluster ``` $ helm uninstall smiling-penguin Removed smiling-penguin ``` <!--s--> ## Exercise Create a Dask cluster using Kubernetes [Notebook](https://github.com/SupaeroDataScience/DE/blob/master/notebooks/Kubernetes_Daskhub.ipynb)